CHARGE TRANSPORT AND OXYGEN EXCHANGE IN MIXED CONDUCTING OXIDES
WG4 Members: Jürgen Fleig, Alexander Opitz, Herbert Hutter
homepage: www.cta.tuwien.ac.at/electrochem/
The main goal of the research is a better understanding of the kinetic processes related to ion transport and interfacial ion transfer in mixed conducting oxides. The activities include analysis of electrochemical reactions such as oxygen reduction or hydrogen oxidation as well as experiments for measuring ionic and electronic conductivity and chemical oxygen diffusion. Typically, studies are performed on thin films such as Sr-doped LaCoO3, LaMnO3, LaFeO3, or Fe-doped SrTiO3 prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Moreover, they include measurements on different samples (PZT, YSZ, etc.).
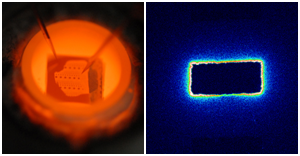
Left: Set-up used for microelectrode studies with tips contacting a microelectrode and the counter electrode. Right: Tracer image obtained after polarizing a rectangular Pt thin film microelectrode on YSZ illustrating high three-phase boundary activity during oxygen reduction.
The main method for analyzing the kinetics of ion transport and reaction in/on oxides is impedance spectroscopy with main emphasis on measurements with microelectrodes and micro-patterned electrodes. This is complemented by tracer diffusion studies with and without additional bias voltage.


